Edmund Optics verwendet Cookies, um dieFunktionen und Inhalte unserer Website zu optimieren und zu verbessern. Miteinem Klick auf „OK“ erhalten Sie die volle Benutzererfahrung. WeitereInformationen über die von uns verwendeten Cookies werden durch Klicken auf„Details“ angezeigt. Wir werden Ihre Daten aus Marketing-Cookies NICHTverkaufen, sondern verwenden sie NUR, um IHRE Erfahrungen mit Edmund Optics zuverbessern.
- Notwendige Cookies werden benötigt, um Grundfunktionen wie die Seitennavigation oder den Zugang zu geschützten Bereichen auf der Webseite zu ermöglichen. Ohne diese Cookies ist die Webseite nicht wie vorgesehen nutzbar.
- Cookiebot1Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen AnbieterCookieConsentSpeichert den Zustimmungsstatus des Benutzers für Cookies auf der aktuellen Domäne.
- Google3Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter
Ein Teil der Daten, die dieser Anbieter gesammelt hat, dient der Personalisierung und der Messung der Werbewirksamkeit.
test_cookieVerwendet, um zu überprüfen, ob der Browser des Benutzers Cookies unterstützt.rc::aDieser Cookie wird verwendet, um zwischen Menschen und Bots zu unterscheiden. Dies ist vorteilhaft für die Website, um gültige Berichte über die Nutzung Ihrer Website zu erstellen.rc::cDieser Cookie wird verwendet, um zwischen Menschen und Bots zu unterscheiden. - LinkedIn2Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen AnbieterbcookieAnstehendli_gcAnstehend
- edmundoptics.com
eogo.edmundoptics.com
radar.cloudflare.com3__cf_bm [x3]Dieser Cookie wird verwendet, um zwischen Menschen und Bots zu unterscheiden. Dies ist vorteilhaft für die Website, um gültige Berichte über die Nutzung Ihrer Website zu erstellen. - edmundoptics.de1QuoteIDSpeichert die ID der Angebotsanfrage.
- eogo.edmundoptics.com1BIGipServer#Verwendet, um Verkehr auf der Website auf mehreren Servern zu verteilen, um die Antwortzeiten zu optimieren.
- productimages.edmundoptics.com
www.edmundoptics.de4AWSALB [x2]Registriert, welcher Server-Cluster den Besucher bedient. Dies wird im Zusammenhang mit Load Balancing verwendet, um die Nutzererfahrung zu optimieren.AWSALBCORS [x2]Registriert, welcher Server-Cluster den Besucher bedient. Dies wird im Zusammenhang mit Load Balancing verwendet, um die Nutzererfahrung zu optimieren. - service.mtcaptcha.com1mtv1ConfSumDieser Cookie wird verwendet, um zwischen Menschen und Bots zu unterscheiden.
- www.edmundoptics.de3.AspNetCore.Antiforgery.#Hilft, Cross-Site Request Forgery- (CSRF-) Angriffe zu verhindern..AspNetCore.Mvc.CookieTempDataProviderBehält die Zustände des Benutzers bei allen Seitenanfragen bei.UMB_SESSIONSpeichert das Domain-Präfix, um festzustellen, ob es https- oder http-URL-Eigenschaften enthält.
- Cookiebot
- Cookies zur Präferenz speichern benuterdefinizierte Informationen und ermöglichen es, die Webseite an den Nutzer anzupassen, beispielsweise die von Ihnen gewählte Sprache oder Region.
- LinkedIn1Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen AnbieterlidcAnstehend
- LiveChat3Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter__lc_cidNotwendig für die Funktionalität der Chat-Box-Funktion der Webseite.__lc_cstNotwendig für die Funktionalität der Chat-Box-Funktion der Webseite.__oauth_redirect_detectorErmöglicht der Webseite, den Besucher zu erkennen, um die Chat-Box-Funktionalität zu optimieren.
- edmundoptics.de1chatEngagedZeigt an, ob der Benutzer die Chat-Funktion der Webseite genutzt hat, um zu bestimmen, ob ihm Chat-Einladungen angezeigt werden sollen.
- LinkedIn
- Diese Cookies ermöglichen den Webseite-Betreibern, das Nutzerverhalten der Besucher zu analysieren, indem Daten anonym gesammelt werden.
- Convert Insight3Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter_conv_rDieses Cookie wird als Referral-Cookie benutzt, in dem das Profil des Besuchers gespeichert ist – das Cookie wird überschrieben, wenn der Besucher die Website erneut aufruft und neue Informationen über den Besucher gesammelt und gespeichert werden._conv_sDieses Cookie enthält einen ID-String über die aktuelle Sitzung. Dieser beinhaltet nicht personenbezogene Informationen über die Unterseiten, die der Besucher aufruft – diese Informationen werden benutzt, um die Nutzererfahrung des Besuchers zu optimieren._conv_vDieses Cookie wird benutzt, um die Häufigkeit und die Dauer der Website-Besuche festzustellen. Das Cookie wird ebenfalls dafür benutzt, um festzustellen, wie viele und welche Unterseiten der Besucher auf einer Website aufruft – diese Informationen können von der Website benutzt werden, um die Domain und die dazugehörigen Unterseiten zu optimieren.
- Livechat1Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter_livechat_has_visitedIdentifiziert den Besucher über Geräte und Besuche hinweg, um die Chatbox-Funktion auf der Webseite zu optimieren.
- edmundoptics.de2ce_diff_timeWird von Crazy Egg zum Zeitversatz für Analysezwecke verwendet.ce_ip_addressWird von Crazy Egg verwendet, um die IP-Adresse des Nutzers zu speichern.
- Convert Insight
- Marketing-Cookies speichern Informationen hinsichtlich anderer besuchter Webseiten. Die Cookies werden genutzt, um auf den Nutzer abgestimmte Werbeanzeigen einzublenden und sind daher für Verlage und externe (Dritte) Werbetreibende relevant.
- Meta Platforms, Inc.4Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen AnbieterlastExternalReferrerErmittelt, wie der Nutzer die Website erreicht hat, indem seine letzte URL-Adresse registriert wird.lastExternalReferrerTimeErmittelt, wie der Nutzer die Website erreicht hat, indem seine letzte URL-Adresse registriert wird.topicsLastReferenceTimeSammelt websiteübergreifende Daten über den Besucher - Diese Daten werden verwendet, um die Relevanz der Werbung zu erhöhen._fbpWird von Facebook genutzt, um eine Reihe von Werbeprodukten anzuzeigen, zum Beispiel Echtzeitgebote dritter Werbetreibender.
- Convert Insight2Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieterconv_randDieses Cookie wird vom Betreiber der Website im Zusammenhang mit multivariaten Tests verwendet. Dies ist ein Werkzeug, mit dem Inhalte auf der Website kombiniert oder geändert werden können. Dies ermöglicht es der Website, die beste Variante/Edition der Website zu finden._conv_sptestDieses Cookie wird vom Betreiber der Website im Zusammenhang mit multivariaten Tests verwendet. Dies ist ein Werkzeug, mit dem Inhalte auf der Website kombiniert oder geändert werden können. Dies ermöglicht es der Website, die beste Variante/Edition der Website zu finden.
- Google7Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter
Ein Teil der Daten, die dieser Anbieter gesammelt hat, dient der Personalisierung und der Messung der Werbewirksamkeit.
IDEAnstehend_gaWird verwendet, um Daten zu Google Analytics über das Gerät und das Verhalten des Besuchers zu senden. Erfasst den Besucher über Geräte und Marketingkanäle hinweg._ga_#Wird verwendet, um Daten zu Google Analytics über das Gerät und das Verhalten des Besuchers zu senden. Erfasst den Besucher über Geräte und Marketingkanäle hinweg._gcl_auWird verwendet, um die Effizienz der Werbeaktivitäten der Website zu messen, indem Daten über die Conversion-Rate der Anzeigen der Website über mehrere Websites hinweg gesammelt werden.NIDAnstehendpagead/1p-user-list/#Wird verwendet, um zu tracken, ob der Besucher Interesse an bestimmten Produkten oder Ereignissen auf mehreren Websites gezeigt hat und wie der Besucher zwischen den Websites navigiert - Dies wird zur Messung des Werbeaufwands verwendet und erleichtert die Zahlung von Empfehlungsgebühren zwischen Websites._gcl_lsVerfolgt die Konversionsrate zwischen dem Nutzer und den Werbebannern auf der Website - Dies dient der Optimierung der Relevanz der Werbung auf der Website. - LinkedIn1Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieterli_sugrAnstehend
- Marketo1Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter_mkto_trkEnthält Daten zum Besucherverhalten und zur Webseite-Interaktion. Dies wird im Zusammenhang mit dem E-Mail-Marketingdienst Marketo.com verwendet, der es der Webseite ermöglicht, Besucher per E-Mail anzusprechen.
- Wisepops14Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieterwisepops [x2]Wird im Zusammenhang mit Popup-Werbeinhalgten verwendet - Das Cookie wird verwendet um zu bestimmen, welche Anzeigen dem Besucher angezeigt werden sollen, und um sicherzustellen, dass dieselben Anzeigen nicht mehr als vorgesehen angezeigt werden.wisepops_props [x2]Wird im Zusammenhang mit Popup-Werbeinhalgten verwendet - Das Cookie wird verwendet um zu bestimmen, welche Anzeigen dem Besucher angezeigt werden sollen, und um sicherzustellen, dass dieselben Anzeigen nicht mehr als vorgesehen angezeigt werden.wisepops_session [x2]Wird im Zusammenhang mit Popup-Werbeinhalgten verwendet - Das Cookie wird verwendet um zu bestimmen, welche Anzeigen dem Besucher angezeigt werden sollen, und um sicherzustellen, dass dieselben Anzeigen nicht mehr als vorgesehen angezeigt werden.wisepops_visitor [x2]Legt eine eindeutige ID für den Besucher fest, die es Third-Party-Advertisern ermöglicht, den Besucher mit relevanter Werbung anzusprechen. Dieser Pairing-Service wird von Werbe-Hubs von Third Parties bereitgestellt, die Echtzeitgebote für Advertiser ermöglichen.wisepops_visits [x2]Wird im Zusammenhang mit Popup-Werbeinhalgten verwendet - Das Cookie wird verwendet um zu bestimmen, welche Anzeigen dem Besucher angezeigt werden sollen, und um sicherzustellen, dass dieselben Anzeigen nicht mehr als vorgesehen angezeigt werden.wisepops_session_idLegt eine eindeutige ID für die Sitzung fest. Dadurch kann die Webseite Daten über Besucherverhalten für statistische Zwecke erhalten.wisepops_session_landing_urlSpeichert die Navigation der Besucher durch die Registrierung von Landing Pages - Dies ermöglicht der Webseite, relevante Produkte zu präsentieren und / oder ihre Werbeeffizienz auf anderen Webseiten zu messen.wisepops_session_referrerSammelt Daten über das Verhalten und die Interaktion von Besuchern. Dies wird verwendet, um Werbung auf der Website relevanter zu machen. Der Cookie erlaubt der Website auch, Verweise von anderen Websiten zu erkennen.wisepops-pageview_idDieses Cookie wird benutzt, um festzustellen, wann der Besucher zuletzt eine andere Unterseite auf der Website besucht hat – das Cookie wird auch einen Zeitstempel erstellen, wenn die Sitzung beginnt.
- YouTube22Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter#-#Wird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.__Secure-ROLLOUT_TOKENAnstehendiU5q-!O9@$Registriert eine eindeutige ID, um Statistiken der Videos von YouTube, die der Benutzer gesehen hat, zu behalten.LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEYWird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.LogsDatabaseV2:V#||LogsRequestsStoreWird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.nextIdWird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.remote_sidNotwendig für die Implementierung und Funktionalität von YouTube-Videoinhalten auf der Website.requestsWird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.ServiceWorkerLogsDatabase#SWHealthLogNotwendig für die Implementierung und Funktionalität von YouTube-Videoinhalten auf der Website.TESTCOOKIESENABLEDWird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.VISITOR_INFO1_LIVEAnstehendYSCAnstehendytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEYWird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.YtIdbMeta#databasesWird verwendet, um die Interaktion der Nutzer mit eingebetteten Inhalten zu verfolgen.yt-player-user-settingsAnstehendyt-remote-cast-availableSpeichert die Benutzereinstellungen beim Abruf eines auf anderen Webseiten integrierten Youtube-Videosyt-remote-cast-installedSpeichert die Benutzereinstellungen beim Abruf eines auf anderen Webseiten integrierten Youtube-Videosyt-remote-connected-devicesSpeichert die Benutzereinstellungen beim Abruf eines auf anderen Webseiten integrierten Youtube-Videosyt-remote-device-idSpeichert die Benutzereinstellungen beim Abruf eines auf anderen Webseiten integrierten Youtube-Videosyt-remote-fast-check-periodSpeichert die Benutzereinstellungen beim Abruf eines auf anderen Webseiten integrierten Youtube-Videosyt-remote-session-appSpeichert die Benutzereinstellungen beim Abruf eines auf anderen Webseiten integrierten Youtube-Videosyt-remote-session-nameSpeichert die Benutzereinstellungen beim Abruf eines auf anderen Webseiten integrierten Youtube-Videos
- edmundoptics.de6_gaexpDieses Cookie wird von Google Analytics verwendet, um festzustellen, ob der Besucher an ihren Marketing-Experimenten beteiligt ist.gwccErmöglicht Google Website Call Conversions - Hier wird registriert, ob der Besucher innerhalb der "Kontakt"-Unterseite auf „Anruf“ geklickt hat. Diese Information wird für Marketing und statistische Zwecke verwendet.mTracking-Pixel, die von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics verwendet werden, um das Webseiten-Engagement zu verfolgen.NWBWird von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics für Webanalysen verwendet, die Webseiten-Traffic verfolgen und speichern.NWB_LEGACYWird von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics für Webanalysen verwendet, die Webseiten-Traffic verfolgen und speichern.wcs_btWird von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics für standortübergreifende Webanalysen verwendet.
- Meta Platforms, Inc.
- Nicht klassifizierte Cookies befinden sich im Status der Untersuchung und werden gemeinsam mit Anbietern von individuellen Cookies klassifiziert.
- Livechat2Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter@@lc_auth_token:3b0f44ba-5eb5-4bb1-a9e1-2214776a186bAnstehend3b0f44ba-5eb5-4bb1-a9e1-2214776a186b:stateAnstehend
- Wisepops2Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieterwisepops_tldAnstehendwisepops-uses-attentionAnstehend
- service.mtcaptcha.com2jsVAnstehendmtv1PulseAnstehend
- Livechat
Cookies sind Textinformationen, die von Webseiten ausgelesen werden können, um das Nutzererlebnis effizienter zu gestalten.
Das Gesetz erlaubt, dass wir Cookies auf Ihrem Gerät speichern dürfen, die für eine ordnungsgemäße Funktionsweise dieser Webseite erforderlich sind. Für alle weiteren Arten von Cookies benötigen wir Ihre Einwilligung.
Diese Webseite nutzt unterschiedliche Arten von Cookies. Manche Cookies auf unserer Seite ermöglichen Tracking-Technologien von Dritten.
Sie können zu jeder Zeit Ihre Cookie-Zustimmung ändern oder Ihre Einwilligung unter unseren Cookie-Einstellungen zurückziehen.
Erfahren Sie mehr über uns, wie Sie uns kontaktieren können oder wie wir personenbezogene Informationen verarbeiten in unserer Datenschutzrichtlinie.
Bitte geben Sie Ihre Einwilligungs-ID und das Datum an, falls Sie uns hinsichtlich Ihrer Zustimmungserklärung kontaktieren.
Bei den meisten Web-Browsern können Sie Ihre Cookies in den Browser-Einstellungen einsehen - meistens im Tab "Datenschutz" oder "Sicherheit". Manche Browser ermöglichen das Löschen von bestimmten Cookies oder verhindern sogar, dass diese erstellt werden. Obwohl das Blockieren von Cookies in Ihrem Browser ein höheres Maß an Datenschutz erzeugen kann, wird dies nicht empfohlen, da viele Webseiten Cookies benötigen, um einwandfrei funktionieren zu können. Alternativ können Sie diese Seite www.aboutcookies.org besuchen, die Ihnen zeigt, wie Sie Cookies in den bekannten Browsern blockieren oder löschen können.













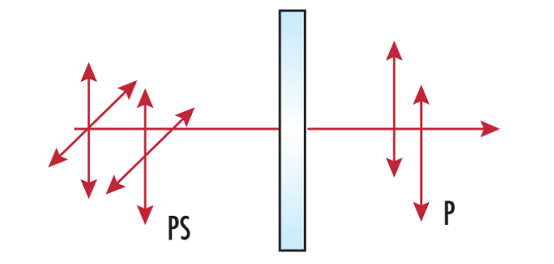
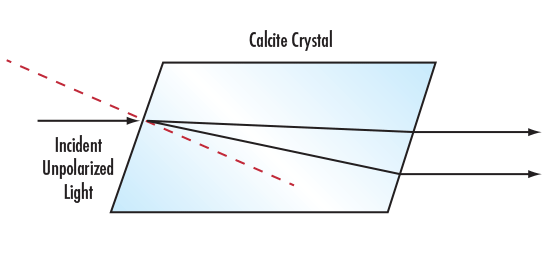





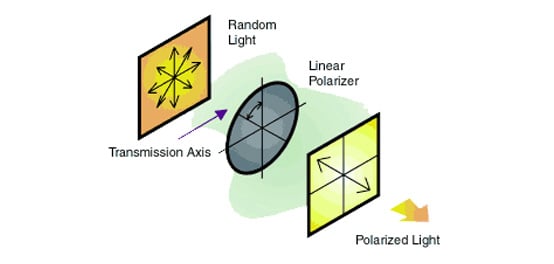





weitere regionale Telefonnummern
ANGEBOTSTOOL
Geben Sie zum Starten die Produktnummer ein.
Copyright 2023 | Edmund Optics, Ltd Unit 1, Opus Avenue, Nether Poppleton, York, YO26 6BL, UK
DATENSCHUTZRICHTLINIE | COOKIE POLICY | AGB | AGB FÜR B2C | IMPRESSUM | BARRIEREFREIHEIT
Die Edmund Optics GmbH Deutschland fungiert als Handelsvermittler für die Edmund Optics Ltd. in Großbritannien.
Vertragspartner ist die Edmund Optics Ltd. in Großbritannien.