
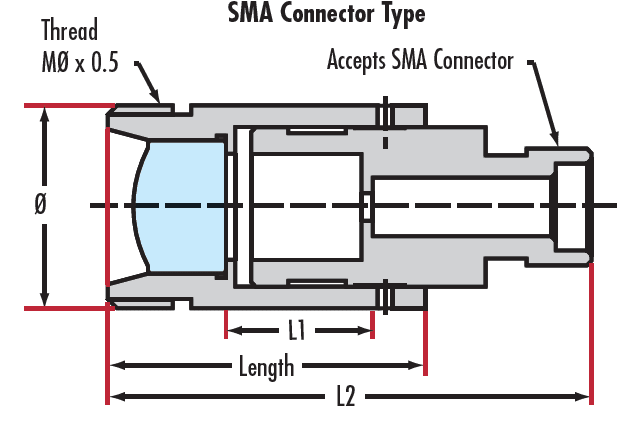
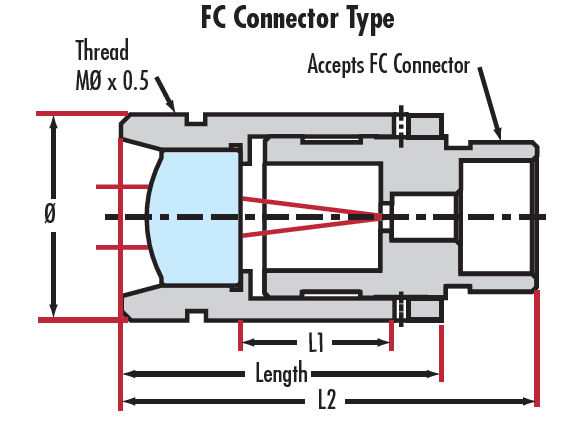
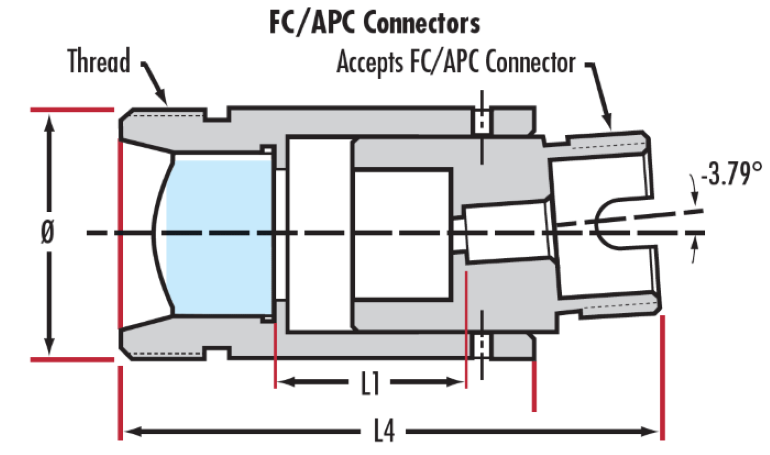
LightPath® Optiken zur Kollimation von Faseroptiken können eingesetzt werden, um Licht aus Fasern auf einen bestimmten Strahldurchmesser / eine bestimmte Punktgröße zu kollimieren oder (bei umgekehrtem Einsatz) um Licht in eine Faser zu fokussieren. Die Linsen sind beugungsbegrenzt und erreichen Punktgrößen bis zu wenigen Mikrometern. Außerdem haben die Linsen eine Antireflexbeschichtung, die für geringe Rückreflexionen sorgt. LightPath® Optiken zur Kollimation von Faseroptiken können als Paar eingesetzt werden, um Eingangs- und Ausgangslicht von Faseroptiken zu koppeln. Eine optimale Leistung für den Langzeiteinsatz wird durch die werkseitig eingestellte und getestete Linsenausrichtung gewährleistet. Typische Anwendungen sind der Einsatz mit fasergekoppelten Lasern sowie Kommunikation und Datentransfer.
1-800-363-1992
weitere regionale Telefonnummern
ANGEBOTSTOOL
Geben Sie zum Starten die Produktnummer ein.
Copyright 2025 | Edmund Optics, Ltd Unit 1, Opus Avenue, Nether Poppleton, York, YO26 6BL, UK
Die Edmund Optics GmbH Deutschland fungiert als Handelsvermittler für die Edmund Optics Ltd. in Großbritannien.
Vertragspartner ist die Edmund Optics Ltd. in Großbritannien.