Edmund Optics verwendet Cookies, um dieFunktionen und Inhalte unserer Website zu optimieren und zu verbessern. Miteinem Klick auf „OK“ erhalten Sie die volle Benutzererfahrung. WeitereInformationen über die von uns verwendeten Cookies werden durch Klicken auf„Details“ angezeigt. Wir werden Ihre Daten aus Marketing-Cookies NICHTverkaufen, sondern verwenden sie NUR, um IHRE Erfahrungen mit Edmund Optics zuverbessern.
- Notwendige Cookies werden benötigt, um Grundfunktionen wie die Seitennavigation oder den Zugang zu geschützten Bereichen auf der Webseite zu ermöglichen. Ohne diese Cookies ist die Webseite nicht wie vorgesehen nutzbar.
- Cloudflare1Erfahren Sie mehr über diesen Anbieter__cf_bmDieser Cookie wird verwendet, um zwischen Menschen und Bots zu unterscheiden. Dies ist vorteilhaft für die Website, um gültige Berichte über die Nutzung Ihrer Website zu erstellen.
- edmundoptics.de1QuoteIDSpeichert die ID der Angebotsanfrage.
- www.edmundoptics.de1CookieConsentSpeichert den Zustimmungsstatus des Benutzers für Cookies auf der aktuellen Domäne.
- Cloudflare
- Cookies zur Präferenz speichern benuterdefinizierte Informationen und ermöglichen es, die Webseite an den Nutzer anzupassen, beispielsweise die von Ihnen gewählte Sprache oder Region.
- edmundoptics.de1chatEngagedZeigt an, ob der Benutzer die Chat-Funktion der Webseite genutzt hat, um zu bestimmen, ob ihm Chat-Einladungen angezeigt werden sollen.
- edmundoptics.de
- Diese Cookies ermöglichen den Webseite-Betreibern, das Nutzerverhalten der Besucher zu analysieren, indem Daten anonym gesammelt werden.
- edmundoptics.de2ce_diff_timeWird von Crazy Egg zum Zeitversatz für Analysezwecke verwendet.ce_ip_addressWird von Crazy Egg verwendet, um die IP-Adresse des Nutzers zu speichern.
- edmundoptics.de
- Marketing-Cookies speichern Informationen hinsichtlich anderer besuchter Webseiten. Die Cookies werden genutzt, um auf den Nutzer abgestimmte Werbeanzeigen einzublenden und sind daher für Verlage und externe (Dritte) Werbetreibende relevant.
- edmundoptics.de6_gaexpDieses Cookie wird von Google Analytics verwendet, um festzustellen, ob der Besucher an ihren Marketing-Experimenten beteiligt ist.gwccErmöglicht Google Website Call Conversions - Hier wird registriert, ob der Besucher innerhalb der "Kontakt"-Unterseite auf „Anruf“ geklickt hat. Diese Information wird für Marketing und statistische Zwecke verwendet.mTracking-Pixel, die von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics verwendet werden, um das Webseiten-Engagement zu verfolgen.NWBWird von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics für Webanalysen verwendet, die Webseiten-Traffic verfolgen und speichern.NWB_LEGACYWird von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics für Webanalysen verwendet, die Webseiten-Traffic verfolgen und speichern.wcs_btWird von der südkoreanischen Firma Naver Analytics für standortübergreifende Webanalysen verwendet.
- edmundoptics.de
- Nicht klassifizierte Cookies befinden sich im Status der Untersuchung und werden gemeinsam mit Anbietern von individuellen Cookies klassifiziert.
Wir nutzen diese Cookie-Typen nicht.
Cookies sind Textinformationen, die von Webseiten ausgelesen werden können, um das Nutzererlebnis effizienter zu gestalten.
Das Gesetz erlaubt, dass wir Cookies auf Ihrem Gerät speichern dürfen, die für eine ordnungsgemäße Funktionsweise dieser Webseite erforderlich sind. Für alle weiteren Arten von Cookies benötigen wir Ihre Einwilligung.
Diese Webseite nutzt unterschiedliche Arten von Cookies. Manche Cookies auf unserer Seite ermöglichen Tracking-Technologien von Dritten.
Sie können zu jeder Zeit Ihre Cookie-Zustimmung ändern oder Ihre Einwilligung unter unseren Cookie-Einstellungen zurückziehen.
Erfahren Sie mehr über uns, wie Sie uns kontaktieren können oder wie wir personenbezogene Informationen verarbeiten in unserer Datenschutzrichtlinie.
Bitte geben Sie Ihre Einwilligungs-ID und das Datum an, falls Sie uns hinsichtlich Ihrer Zustimmungserklärung kontaktieren.
Bei den meisten Web-Browsern können Sie Ihre Cookies in den Browser-Einstellungen einsehen - meistens im Tab "Datenschutz" oder "Sicherheit". Manche Browser ermöglichen das Löschen von bestimmten Cookies oder verhindern sogar, dass diese erstellt werden. Obwohl das Blockieren von Cookies in Ihrem Browser ein höheres Maß an Datenschutz erzeugen kann, wird dies nicht empfohlen, da viele Webseiten Cookies benötigen, um einwandfrei funktionieren zu können. Alternativ können Sie diese Seite www.aboutcookies.org besuchen, die Ihnen zeigt, wie Sie Cookies in den bekannten Browsern blockieren oder löschen können.











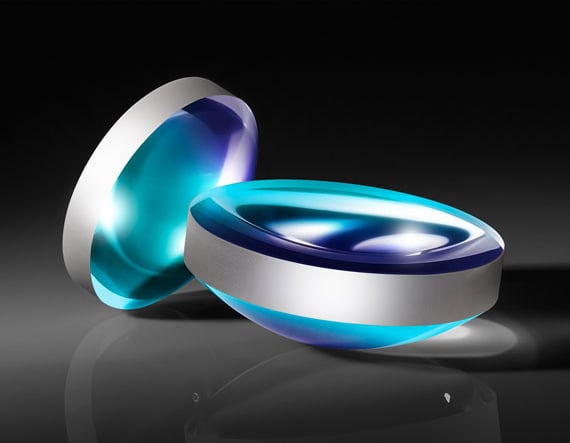
 Kurven:pdf
Kurven:pdf
 Zemax:zar
Zemax:zar
 eDrawing:eprt
eDrawing:eprt
 Code-V-Datei:seq
Code-V-Datei:seq
 EO Spec Sheet
EO Spec Sheet
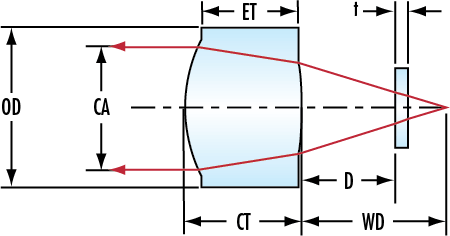










































weitere regionale Telefonnummern
ANGEBOTSTOOL
Geben Sie zum Starten die Produktnummer ein.
Copyright 2023 | Edmund Optics, Ltd Unit 1, Opus Avenue, Nether Poppleton, York, YO26 6BL, UK
Die Edmund Optics GmbH Deutschland fungiert als Handelsvermittler für die Edmund Optics Ltd. in Großbritannien.
Vertragspartner ist die Edmund Optics Ltd. in Großbritannien.